Gerard O’Neill
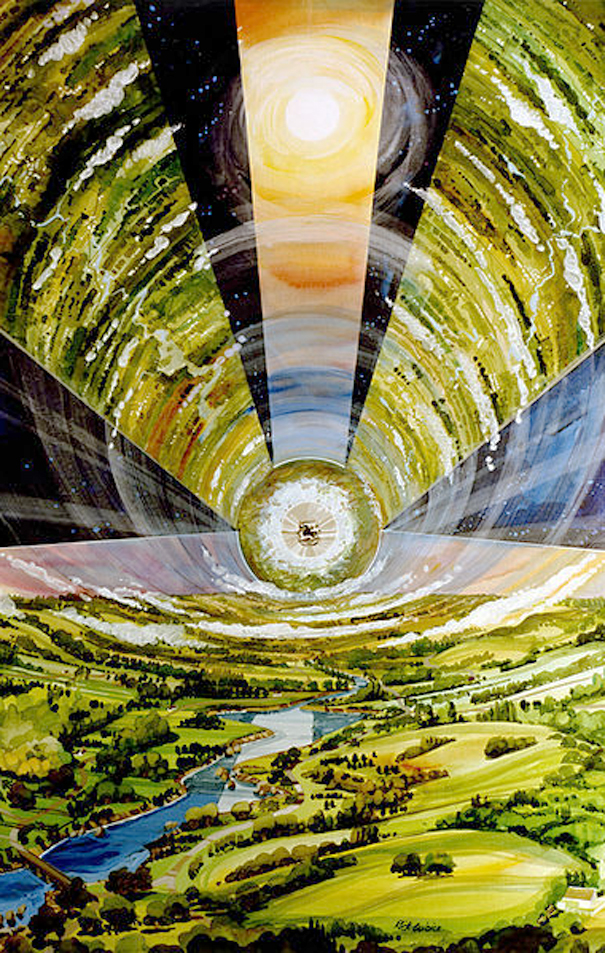
O’Neill cylinder
O’Neill was inspired by the papers written by his students. He began to work out the details of a program to build self-supporting space habitats in free space.Among the details was how to provide the inhabitants of a space colony with an Earth-like environment. His students had designed giant pressurized structures, spun up to approximate Earth gravity by centrifugal force . With the population of the colony living on the inner surface of a sphere or cylinder, these structures resembled “inside-out planets”. He found that pairing counter-rotating cylinders would eliminate the need to spin them using rockets.This configuration has since been known as the O’Neill cylinder.