FILE SÃO PAULO 2025: SYNTHETIKA – Frederik De Wilde
Hunter and Dog
Frederik De Wilde
FILE SÃO PAULO 2025: SYNTHETIKA – Art and Technology – Installations
Electronic Language International Festival
Hunter and Dog – Belgium
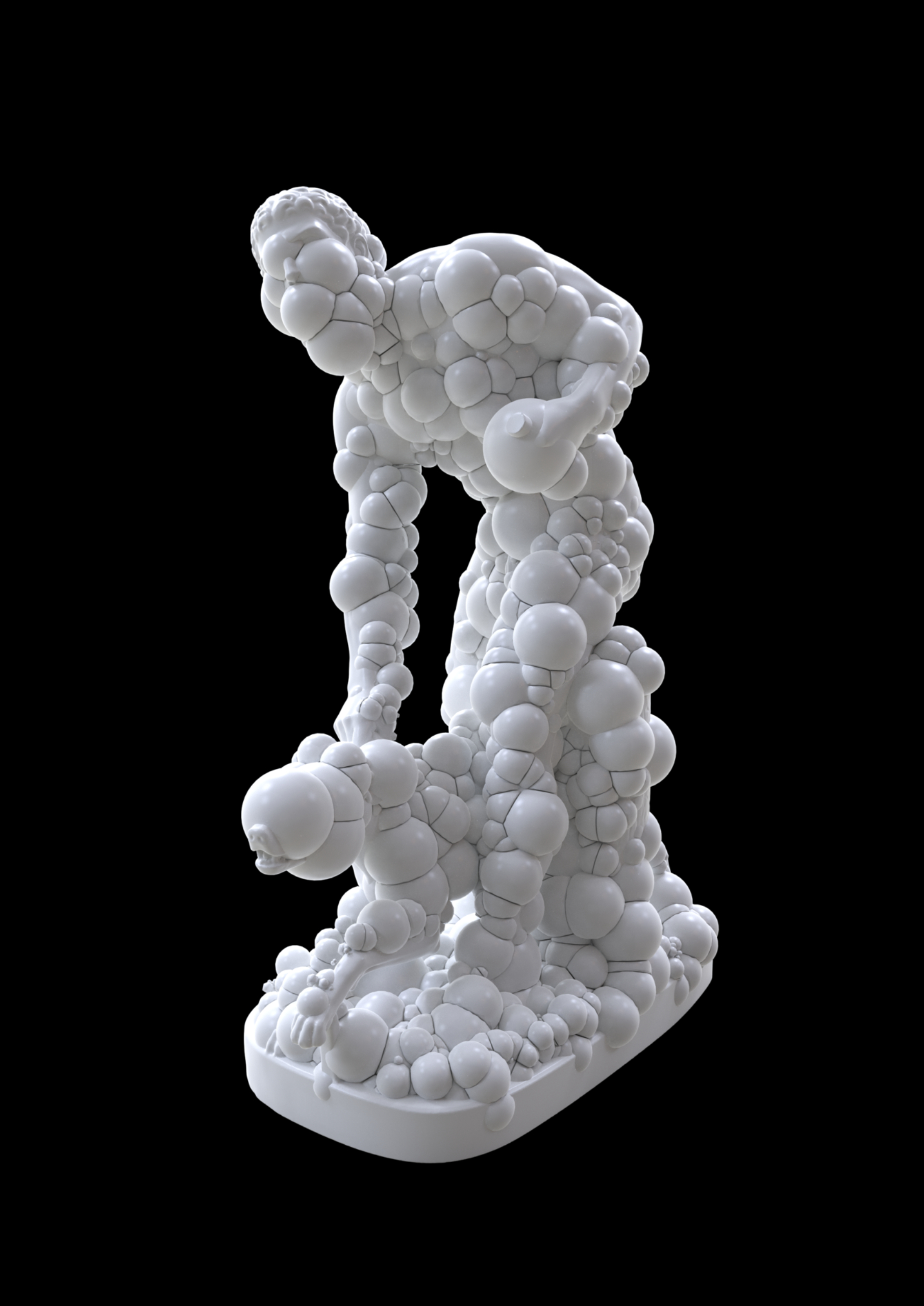
Genetic and evolutionary algorithms reinterpret an existing artwork. De Wilde uses digital scans and custom genetic and evolutionary algorithms as a deconstruction technique to reinterpret and update the nineteenth-century work Hunter and Dog from sculptor John Gibson R. A. (1790–1866).
Frederik De Wilde’s Hunter and Dog interrogates the intersections of human evolution, genetic engineering, and the hybridization of technology and biology. De Wilde reinterprets the historical sculpture through the lens of post-evolutionary theory, engaging with contemporary debates on CRISPR, synthetic biology, and the implications of human-directed genetic modification. CRISPR, the revolutionary gene-editing technology, has introduced an unprecedented rupture in the trajectory of evolution. No longer constrained by the slow mechanisms of natural selection, humans now possess the ability to intervene directly in their own genetic blueprint, marking a shift toward a post-Darwinian paradigm. This technological power, however, is not neutral; it emerges from a historical lineage of scientific inquiry deeply entangled with colonialism. The history of genetic manipulation is inseparable from colonial bioprospecting, eugenics, and exploitative medical experimentation on marginalized populations. Colonial regimes treated bodies—both human and non-human—as sites of intervention, control, and optimization, a logic that persists in contemporary biotechnological frameworks. Post-colonial discourse reveals how genetic engineering risks perpetuating these legacies, reinforcing power asymmetries between those who wield biotechnological control and those subjected to its consequences. CRISPR, while offering the promise of eradicating disease and expanding human potential, also raises ethical concerns about genetic stratification, bio-capitalism, and the commodification of life itself. De Wilde’s work visualizes these tensions, making visible the processes of cell division and morphogenesis—the very biological mechanisms now subject to human intervention. Hunter and Dog does not merely depict the transformation of a neoclassical form but speculates on the future of the human body as a site of engineered evolution. From a decolonial perspective, the artwork questions who has the authority to edit life and to what ends. It challenges the techno-utopian narratives that frame genetic modification as an inevitable progress while obscuring its social, ethical, and ecological implications. By hybridizing art, science, and technology, Hunter and Dog compels us to confront the uncertainties of a CRISPR-driven future: Will genetic editing reinforce existing inequalities, or can it be decolonized and democratized? How do we navigate this post-natural frontier without losing the human—and more-than-human—dimensions of our existence? De Wilde’s work invites us into this speculative space, where the hunter, the dog, and the algorithm coalesce into a vision of a world where biology is no longer destiny, but a site of contested agency.
Where are we going from here?
BIO
Frederik De Wilde fuses art, science, and tech. Known for his Blackest-Black works that inspired Kapoor’s Vantablack, he has shown at Venice Biennale, BOZAR, MAAT, Pompidou, and ZKM, winning awards like Ars Electronica.