QUBIT AI: Banz & Bowinkel
Bots
FILE 2024 | Installations
International Electronic Language Festival
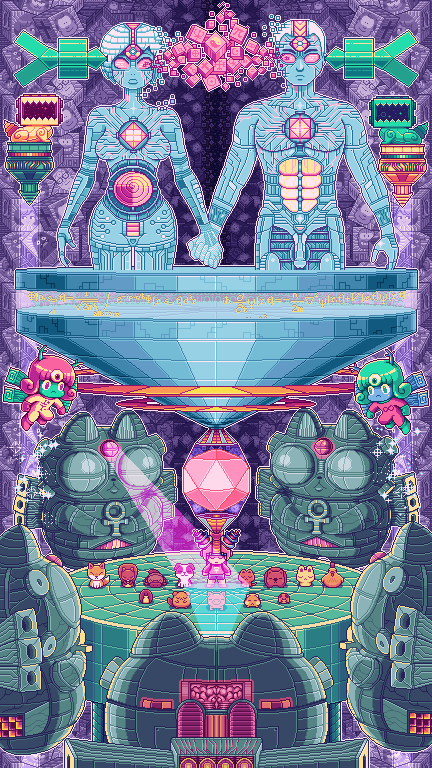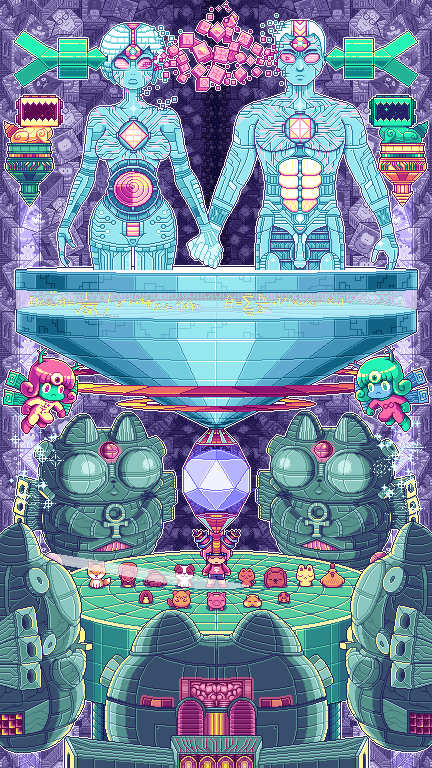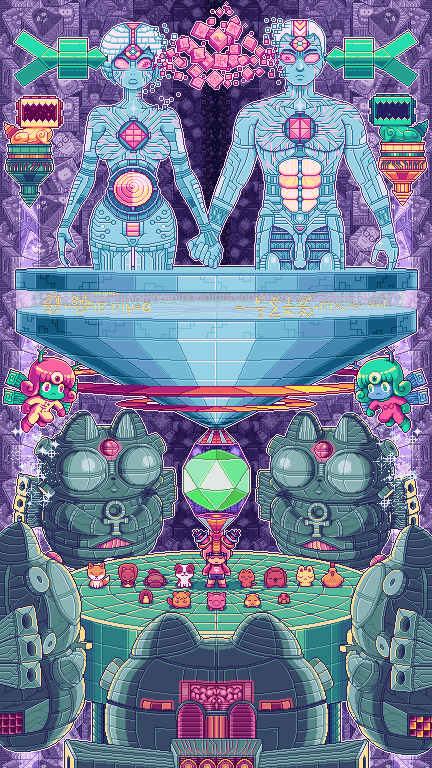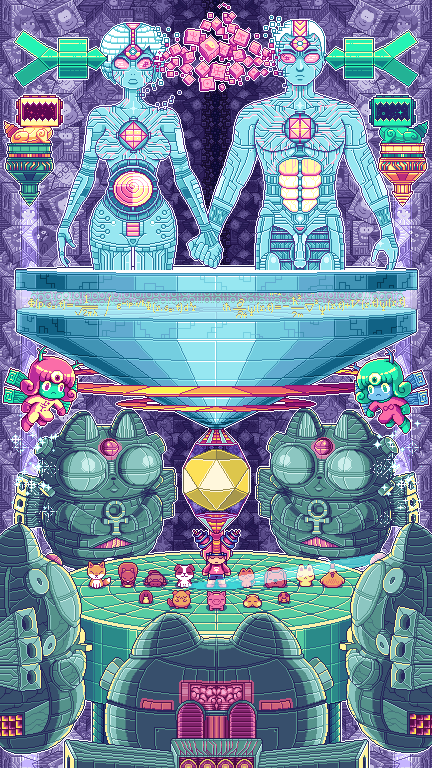
Bots presents a computer-controlled society through a series of algorithmically controlled humanoid avatars that appear on physical carpets using augmented reality (AR). Real-time performances synthesize human behavioral patterns into a formalized digital social study. Omnipresent, combined with our devices and incorporated into virtual environments, the work reminds us of our own digitalized world, in which we are surrounded by invisible bots.
Bio
Giulia Bowinkel (born 1983) and Friedemann Banz (born 1980) live in Berlin and have worked together under the name Banz & Bowinkel since 2009. In 2007 they graduated from the Art Academy with Albert Oehlen and started making art with computers . His work encompasses computer-generated imagery, animation, augmented reality, virtual realities and installations.