


hanson robotics
Sophia the robot
Sofia, le robot humanoïde (android) ultra-réaliste fabriqué par Hanson Robotics, devient le premier robot a obtenir une citoyenneté officielle ! C’est l’Arabie Saoudite qui a officialisé il y a quelques jours l’existence de Sofia, devenant le premier pays à reconnaitre le statut de citoyen d’un robot et d’une intelligence artificielle. Sofia, dont nous avions déjà parlé l’année dernière, est un robot ultra-réaliste capable de tenir une conversation, de reconnaitre les gens et d’interagir avec son environnement, mais surtout possède sa propre personnalité et des expressions faciales réalistes.

FILE 2024 – Call for Entries
The Call for Entries to participate in FILE – Electronic Language International Festival’s projects in 2024 is now open. The festival seeks original artworks in Art and Technology, by Brazilian and international artists. Registration remains open until February 10th. Access the registration form.
FILE is a non-profit cultural organization that has propagated creation and experimentation in Art and Technology through exhibitions, events and publications over 23 years. This call opens up the opportunity to participate in the 23rd. Edition of the Electronic Language International Festival, which is scheduled to take place at the FIESP Cultural Center, in São Paulo. The selected projects will also be able to collaborate in parallel events in different states in Brazil.
Using the registration form, it is possible to send interactive installations, sound art, video art, robotics, animations, CGI videos, virtual realities, augmented realities, mobile art, games, gifs, internet art, lectures and workshops, among others. To participate in the LED SHOW programm, exhibited annually at the FIESP Digital Art Gallery, register using the form. Sign up!

Heinrich Bulthoff
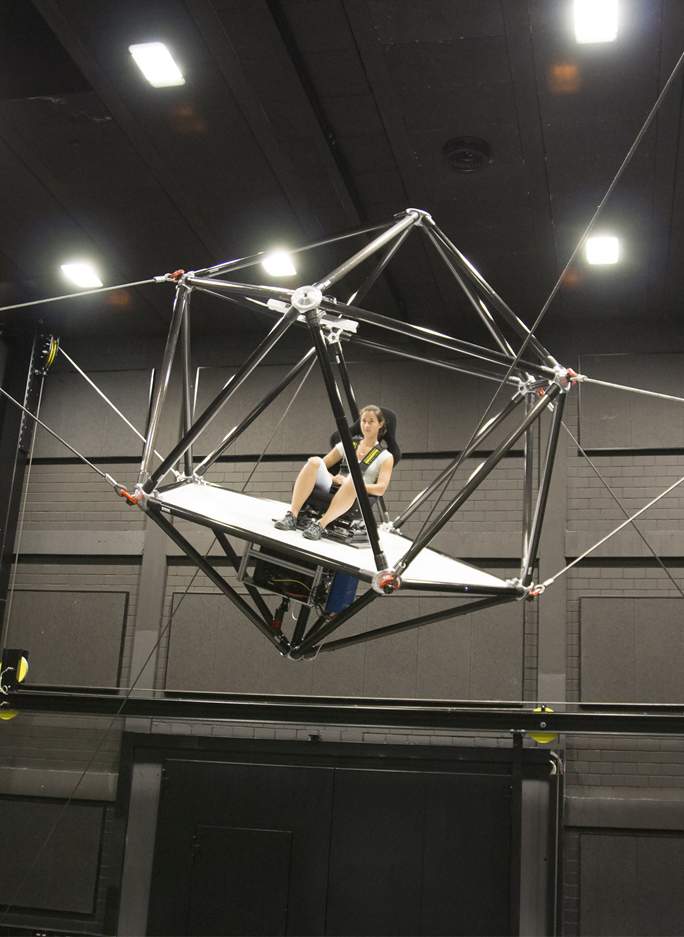
Cable Robot Simulator
Max-Planck-Institut für biologische Kybernetik
Eight steel cables, each with 1.4 tons of tensions, hold aloft a caged platform with a seat for one person. Using a wireless VR headset, that person can simulate experiences like flight while being zoomed in dozens of different ways. Eight retracting cables connected to a winch pull on the cage. It’s like a giant, flying VR jungle gym.

Kino
MIT Media Lab, Stanford University
This work explores a dynamic future where the accessories we wear are no longer static, but are instead mobile, living objects on the body. Engineered with the functionality of 18 robotics, this “living” jewelry roams on unmodified clothing, changing location and reconfiguring appearance according to social context and enabling multitude presentations of self. With the addition of sensor devices, they transition into active devices which can react to environmental conditions. They can also be paired with existing mobile devices to become personalized on-body assistants to help complete tasks. Attached to garments, they generate shape-changing clothing and kinetic pattern designs–creating a new, dynamic fashion.
It is our vision that in the future, these robots will be miniaturized to the extent that they can be seamlessly integrated into existing practices of body ornamentation. With the addition of kinetic capabilities, traditionally static jewelry and accessories will start displaying life-like qualities, learning, shifting, and reconfiguring to the needs and preferences of the wearer, also assisting in fluid presentation of self. We envision a new class of future wearables that possess hybrid qualities of the living and the crafted, creating a new on-body ecology for human-wearable symbiosis.

RAFFAELLO D’ ANDREA AND MAX DEAN
The Robotic Chair
The Robotic Chair is a generic-looking wooden chair with the capacity to fall apart and put itself back together. With shuddering force, the chair collapses to the floor. With persistence and determination, it proceeds to seek out its parts and upright itself. Powered by MICROMO coreless dc motors, The Robotic Chair is distinguished in the world of objects for its capacity to elicit empathy, compassion and hope.

Dragan Ilic
Re)Evolution
With the machine programed to draw, the robot becomes a medium for interaction and for “symbiosis” with the artist, creating a kind of “hybrid body” of man and machine, whose nervous system and brain waves administer “software commands” to the robot during the drawing performance. A key actor in the exhibition will be the new model of the KUKA KR 210 robot, that has a multi-functioning performative role: from drawing, experimental dance, music – through the production of industrial sound, and a six channel video projection that documents Ilić’s projects.

GUTO NÓBREGA
Breathing
File Festival
Breathing is a work of art based on a hybrid creature made of a living organism and an artificial system. The creature responds to its environment through movement, light and the noise of its mechanical parts. Breathing is the best way to interact with the creature.
This work is the result of an investigation of plants as sensitive agents for the creation of art. The intention was to explore new forms of artistic experience through the dialogue of natural and artificial processes. Breathing is a pre-requisite for life, and is the path that links the observer to the creature.Breathing is a small step towards new art forms in which subtle processes of organic and non-organic life may reveal invisible patterns that interconnect us.Breathing is a work of art driven by biological impulse. Its beauty is neither found isolated on the plant nor in the robotic system itself. It emerges at the very moment in which the observer approaches the creature and their energies are exchanged through the whole system. It is in that moment of joy and fascination, in which we find ourselves in a very strange dialogue, that a life metaphor is created.Breathing is the celebration of that moment.

Jordan Wolfson
요르단 울프슨
ジョーダンウォルフソン
Female Figure
The stare of the animatronic sculpture is so intense, it would put anyone uncomfortable. The mask is probably there as a way to avoid creating a human face using animatronics but it also definitely adds to the creepiness of the overall look. The importance of the gaze is found throughout Wolfson’s work but it finds here a very special interpretation. He gives the ability to gaze to two different entities, a stripper and a robot, who are by definition never supposed to look up. The visitor is no longer in control of the situation, creating the awkwardness that is at the core of the work.
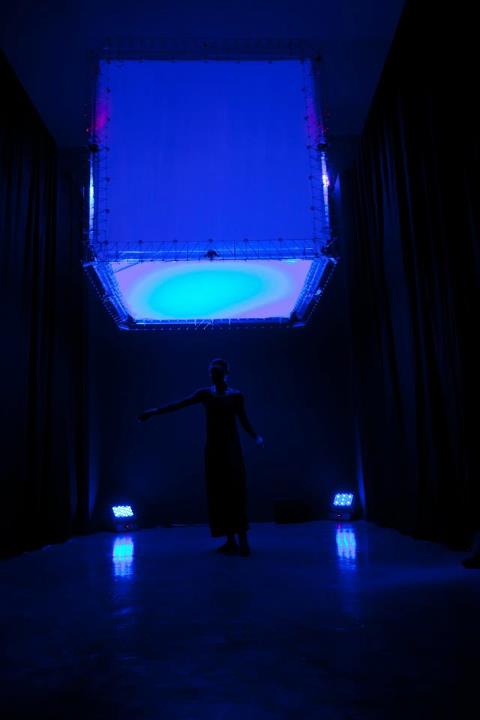

NXI GESTATIO: NICOLAS REEVES, DAVID ST-ONGE & GHISLAINE DOTÉ
Paradoxal Sleep
File Festival
O projeto “Paradoxal Sleep” integra uma série de obras na qual grandes cubos robotizados, medindo 2,25 m3, funcionam como estruturas flutuantes usadas como plataformas para vários projetos multimídia e performances. No FILE 2012, a equipe da NXI GESTATIO apresentará um único cubo que irá se mover nos espaços expositivos. O cubo reajustará constantemente sua posição medindo a distância entre as paredes ao redor.
.
The “Paradoxal Sleep” project integrates a series of works in which large robotic cubes, measuring 2.25 m3, function as floating structures used as platforms for various multimedia projects and performances. At FILE 2012, the NXI GESTATIO team will present a single cube that will move in the exhibition spaces. The cube will constantly readjust its position by measuring the distance between the surrounding walls.
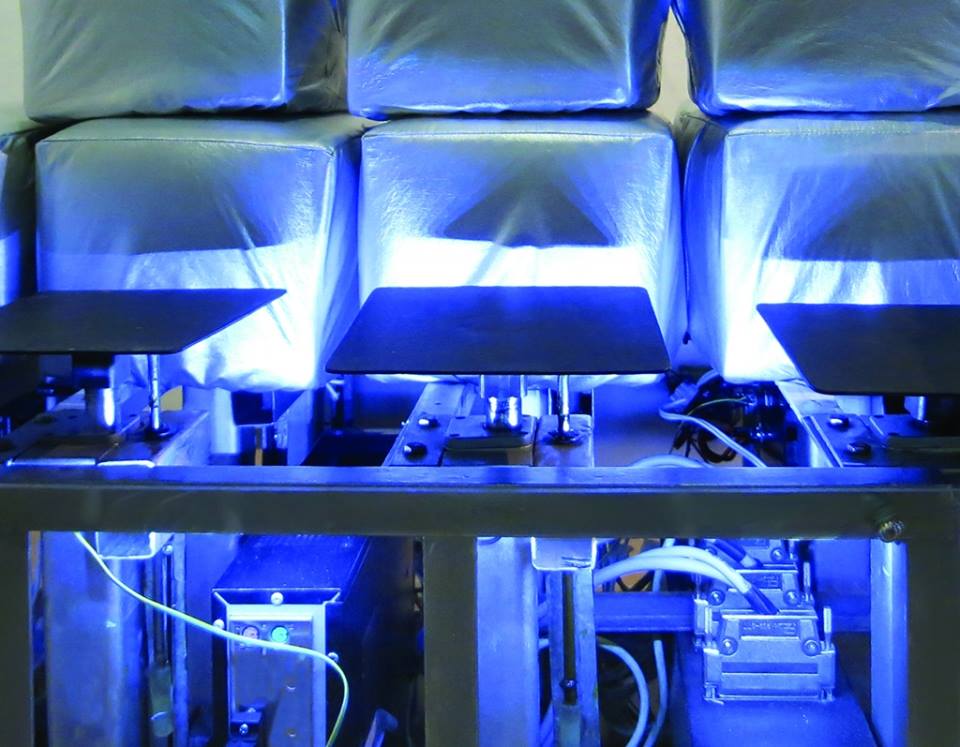

Ricardo Barreto and Maria Hsu Rocha
Martela
FILE Festival
Tactila ist eine Kunstform, deren Medium der Tastsinn (Takt) ist, der von allen anderen unabhängig ist und seine eigene Intelligenz, Vorstellungskraft, Erinnerung, Wahrnehmung und Empfindung hat. Es ist bekannt, dass Bild und Ton in der Kunst und in anderen Disziplinen Vorrang haben. Tactila findet rechtzeitig statt und kann daher aufgezeichnet werden und für spätere Ausführungen verschiedene Notationsformen haben. Deshalb wurde seine Entwicklung dank mechatronischer und Robotersysteme, die mit Maschinensprachen kompatibel sind, erst jetzt möglich. Bei der Erstellung taktiler Werke handelt es sich um eine (Takt-) Komposition, die in handgemachter Notation erstellt und auf einer Tastatur oder direkt darauf gespielt werden kann der Computer der taktilen Maschine (Roboter).
Taktile Maschinen können durch Punkte, Vektoren und Texturen mit unterschiedlichen Rhythmen und Intensitäten zahlreiche taktile Möglichkeiten bieten und an verschiedenen Ausdehnungen und Orten unseres Körpers ausgeführt werden.
Die erste taktile Maschine heißt „Martela“. Es ist ein taktiler Roboter, der aus 27 Motoren besteht, die in drei Quadrate (3 × 3) unterteilt sind, d. H. Jedes Quadrat hat 9 Motoren. Jeder Motor entspricht einem Matrixpunkt, daher haben wir 27 taktile Einheiten, mit denen der Körper des Benutzers mit verschiedenen Intensitäten berührt werden kann.

Engineered Arts
AMECA
“Multiply the power of artificial Intelligence with an artificial body. Ameca is the physical presence that brings your code to life. The most advanced lifelike humanoid you can use to develop and show off your greatest machine learning interactions. This robot is the digital interface to the real world.” Engineered Arts
.
“A U.K. robotics firm called Engineered Arts just debuted the first videos of its new humanoid robot, which is able to make hyper-realistic facial expressions. It’s a pretty stunning achievement in the world of robotics; it just also happens to be absolutely terrifying.
Named Ameca, the robot’s face features eyes, cheeks, a mouth, and forehead that contort and change shape to show off emotions ranging from awe to surprise to happiness. One of the new videos of Ameca shows it waking up and seemingly coming to grips with its own existence for the first time ever.” Neel V.Patel
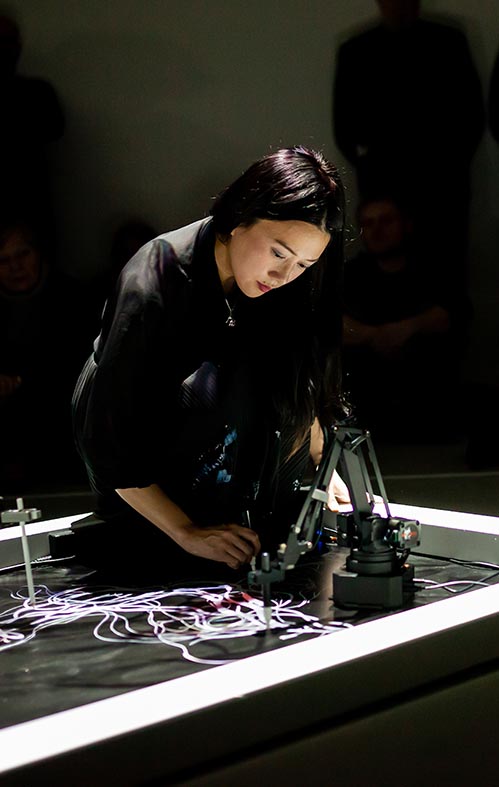
Sougwen Chung
愫君
Drawing Operations
Sougwen Chung is an internationally renowned multidisciplinary artist, who uses hand-draw and computer-generated marks to address the closeness between person-to-person and person-to- machine communication. She is a former researcher at MIT Media Lab and current Artist in Resident at Bell Labs and New Museum of Contemporary Art in New York. Her speculative critical practice spans installation, sculpture, still image, drawing, and performance. Drawing Operations Unit: Generation 1 is the 1st stage of an ongoing study of human and robotic interaction as an artistic collaboration.

Bill Vorn & Louis-Philippe Demers
루이 필립 멀스
Луи-Филипп Демерс
Inferno
“Inferno” est un projet de performance robotique inspiré par la représentation des différents “niveaux de l’enfer”, la particularité de ce projet réside dans le fait que les différentes machines faisant partie du spectacle seront installées sur le corps même des spectateurs.

Daft Punk
Electroma
DAFT PUNK’S ELECTROMA IS THE EAGERLY ANTICIPATED DIRECTORIAL FEATURE FILM DEBUT FROM GUY-MANUEL DE HOMEM-CHRISTO AND THOMAS BANGALTER, BETTER KNOWN TOGETHER AS DAFT PUNK. A PSYCHEDELIC VISUAL AND MUSICAL ODYSSEY, ELECTROMA FOLLOWS THE JOURNEY OF TWO ROBOTS ON THEIR QUEST TO BECOME HUMAN. FEATURING A STUNNING SOUNDTRACK WITH MUSIC FROM TODD RUNDGREN, BRIAN ENO, CURTIS MAYFAIR, SEBASTIEN TELLIER AND CHOPIN, ELECTROMA PLAYS OUT BEAUTIFULLY ‘LIKE MUSIC FOR THE EYES’.
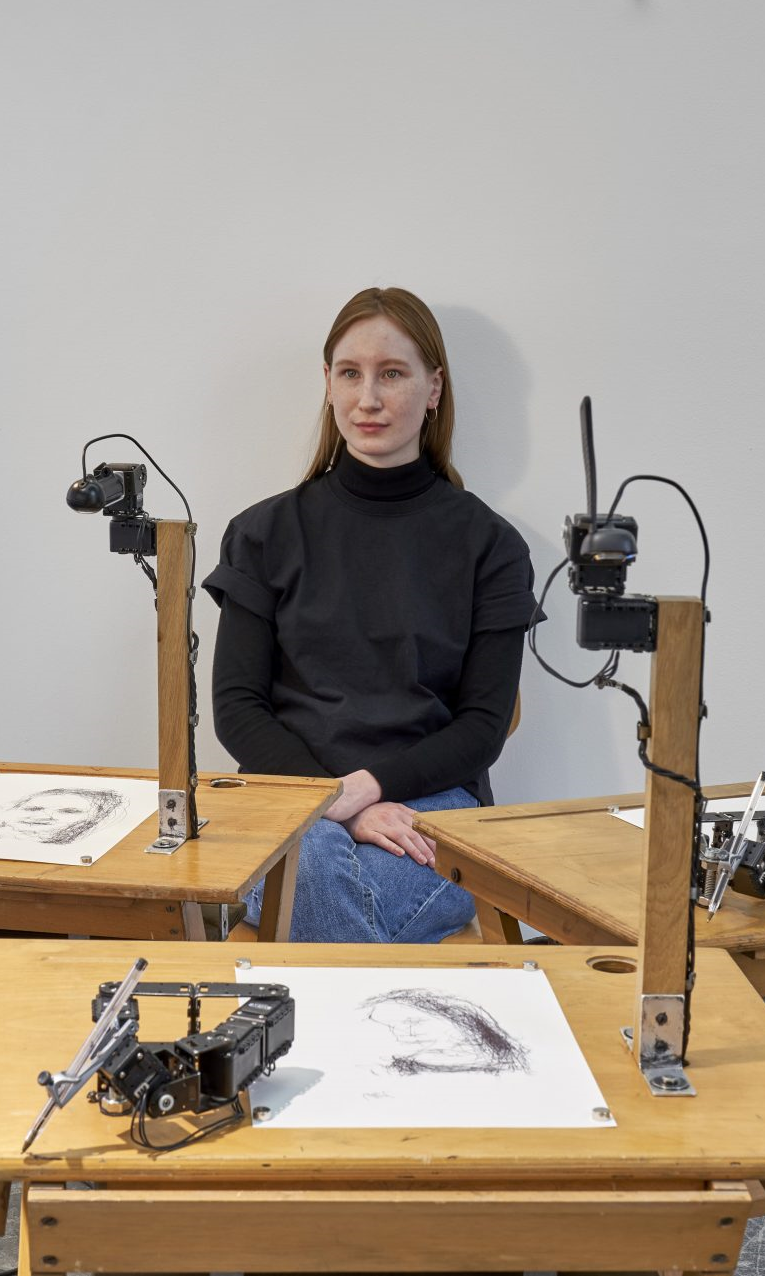

PATRICK TRESSET
Étude humaine #1
L’installation interactive Human Study #1 de Patrick Tresset se compose de trois robots dessinateurs. Les visiteurs peuvent s’asseoir comme des modèles pour être visuellement enregistrés et représentés par les trois machines. Chacun des trois robots dessine dans son propre style et manie le stylo d’une manière différente. A côté du bras de dessin, chaque robot est équipé d’une caméra mobile. Ils les utilisent pour observer alternativement le modèle et le dessin résultant. Tresset n’est pas intéressé à utiliser les robots pour simuler un style de dessin humain. Il examine plutôt les différences entre l’exécution humaine et robotique. Tresset décrit les capacités de ses machines comme « non intelligentes ». Ils donnent seulement l’impression d’agir de leur propre gré. Ils font preuve d’un comportement humain, mais basé sur un programme ne stipulant qu’un ensemble restreint d’actions.

Sun Yuan and Peng Yu
Can’t Help Myself
Constructed of a Kuka industrial robot arm, ‘Can’t Help Myself’ is programmed to do one thing: contain a viscous, deep-red liquid within a fixed area. When the blood-like substance pools too much, this activates the robot’s sensors causing the arm to swivel, flex, and shovel the liquid back to the center leaving splashes and smudges in its wake.

Eric Singer/LEMUR
LEMUR GuitarBot
File Festival
The “LEMUR GuitarBot” is a robotically controlled electric slide guitar-like instrument. It is comprised of four independently controllable units which can pick and slide extremely rapidly. Resembling neither a traditional robot nor a guitar, it is a new type of instrument with markedly different capabilities than a human guitarist.

AURÉLIEN BORY
“Con Sans Objet, volevo introdurre sul palco un robot industriale con la forza di muovere elementi dello scenario oltre che attori. La macchina diventa protagonista a tutti gli effetti. È un braccio articolato e meccanico. È usato come un “burattino” – un essere tecnologico al 100% – nel suo dialogo con un normale uomo contemporaneo “.

MEDIATED MATTER GROUP
Fiberbots
Fiberbots ist eine digitale Fertigungsplattform, die kooperative Roboterherstellung mit der Fähigkeit verbindet, hochentwickelte Materialarchitekturen zu generieren. Die Plattform kann das Design und die digitale Fertigung von großflächigen Strukturen mit hoher räumlicher Auflösung ermöglichen, wobei mobile Fertigungsknoten oder Roboter-Agenten genutzt werden, um die Materialzusammensetzung der im laufenden Betrieb konstruierten Struktur gemäß ihrer Umgebung abzustimmen.

Marcos Mauro
Pasionaria
Pasionaria represents the consequences of our current way of life, as conceived by choreographer Marcos Morau. A future where human beings would have lost their vitality through individualism and transhumanism. The gloomy universe of the spectacle thus seems sanitized of all affect, all passion, and consequently, humanity. All that remains is the labor force that is tirelessly busy vacuuming or handling packages of products. Ringing phones, doors or other objects constantly capture the attention of the protagonists who have become puppets. Manipulated by outside forces, instead of being driven by their deep desires, the humans of this dystopia merge into simple working robots.

Liam Young
Where the City Can’t See
Directed by speculative architect Liam Young and written by fiction author Tim Maughan, ‘Where the City Can’t See’ is the world’s first narrative fiction film shot entirely with laser scanners, designed in collaboration with Alexey Marfin. The computer vision systems of driverless cars google maps, urban management systems and CCTV surveillance are now fundamentally reshaping urban experience and the cultures of our city. Set in the Chinese owned and controlled Detroit Economic Zone (DEZ) and shot using the same scanning technologies used in autonomous vehicles, we see this near future city through the eyes of the robots that manage it. Exploring the subcultures that emerge from these new technologies the film follows a group of young car factory workers across a single night, as they drift through the smart city point clouds in a driverless taxi, searching for a place they know exists but that the map doesn’t show.

Constanza Silva
Silverfish Stream
file festival
The sound generated by the friction of the metallic robots against the floor, like that created by the contact between man and machine, is registered, altered and played in real time by the spheres, each with its own tonality, and amplified in the room. What is generated is a stream of multisensory information (visual, auditive, tactile), natural environment for mechanic creatures.
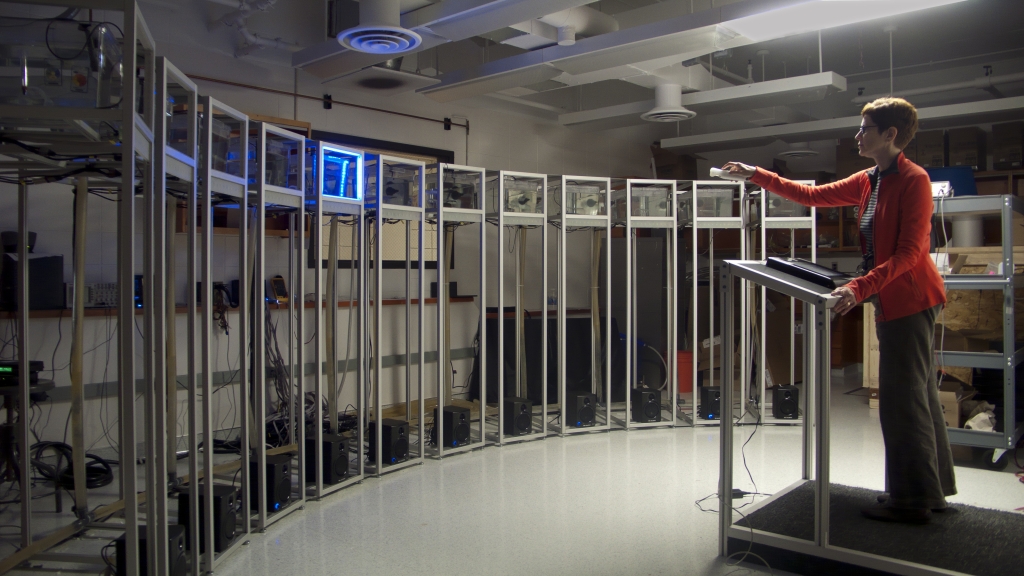

localStyle (Marlena Novak & Jay Alan Yim) in collaboration with Malcolm MacIver
Scale
‘scale’ is an interspecies art project: an audience-interactive installation that involves nocturnal electric fish from the Amazon River Basin. Twelve different species of these fish comprise a choir whose sonified electrical fields provide the source tones for an immersive audiovisual environment. The fish are housed in individual tanks configured in a custom-built sculptural arc of aluminum frames placed around a central podium. The electrical field from each fish is translated into sound, and is thus heard — unprocessed or with digital effects added, with immediate control over volume via a touchscreen panel — through a 12-channel surround sound system, and with LED arrays under each tank for visual feedback. All software is custom-designed. Audience members interact as deejays with the system. Amongst the goals of the project is our desire to foster wider public awareness of these remarkable creatures, their importance to the field of neurological research, and the fragility of their native ecosystem.The project leaders comprise visual/conceptual artist Marlena Novak, composer/sound designer Jay Alan Yim, and neural engineer Malcolm MacIver. MacIver’s research focuses on sensory processing and locomotion in electric fish and translating this research into bio-inspired technologies for sensing and underwater propulsion through advanced fish robots. Novak and Yim, collaborating as ‘localStyle’, make intermedia works that explore perceptual themes, addressing both physical and psychological thresholds in the context of behavior, society/politics, and aesthetics.

SYD MEAD
In 1979, projects began to include work with most major studios, on such feature films as Star Trek: The Motion Picture, followed by, Bladerunner, TRON, 2010, Short Circuit, Aliens, Time Cop, Johnny Mnemonic, Mission Impossible-3, and most recently Elysium starring Jodi Foster and Matt Damon, Directed by Neill Blomkamp. Beginning in 1983, Syd began to develop close working relationships with a number of major Japanese corporate clients, including; Sony, Minolta, Dentsu, Dyflex, Tiger, Seibu, Mitsukoshi, Bandai, NHK and Honda as well as contributing to two Japanese film projects, The New Yamato and Crises 2050. In the 1990s’, Syd supplied designs for two Japanese toy icons, “The New Yamato” and all eight robot characters in the new Turn-A Gundam mobile suite series which were also seen as characters in Television shows.

CHRIS CUNNINGHAM
Björk: All Is Full of Love
The video reaches its harmonious climax as the robots join in embrace, still being detailed by the robotic machines beside them.
Each robot was designed by Cunningham, faces reminiscent of Björk’s own delicate visage. The sterility of the room and lighting and the rendered movements of the machines contrasts with the fluid motions of the robots as they connect in a purely human method.

JORIS STRIJBOS
SVNSCRNS
SVNSCRNS is a commissioning project that is initiated by Klankvorm after a concept by Joris Strijbos. The project consists of the realization of a kinetic audiovisual installation for which artists are invited to realize content. The installation can be used for live performances as well as for playing prearranged compositions. The installation consists of seven rotating projection screens and speakers that can be controlled from a central point. Custom build software and hardware are accessible for artists from different backgrounds to experiment with this new dynamic field for audiovisual composition. Light, sound and movement come together with different forms of digital media to create a multi sensorial experience for the audience. In this way the project functions as a platform in which makers and creators of all kinds can collaboratively explore this kinetic audiovisual medium. The result is a slow moving robotic structure which can display different sorts of media but in it’s presence will have a strong influence on the experience of the spectator.

Geumhyung Jeong
Homemade RC Toy
Her new installation centers on five human-scale, remote-control sculptures that she cobbled together from metal brackets, batteries, wires, dental study props, and disassembled mannequins. Surrounding them are stepped plinths whose bright colors echo the robot sculptures’ wiring. The plinths display fetishistic agglomerations of spare parts: wheels, cables, gutted medical practice torsos, home repair parts. In their default state, the sculptures are frozen, comatose, even if all that wiring and machinery certainly suggests movement. The installation is the setting for a series of live interactions between the artist and her uncanny others.

Nicholas Stedman
After Deep Blue
ADB is a modular robot designed for tactile interactions with people. It is composed of a chain of prism-shaped robotic modules. Through the modules’ coordinated behavior, the robot writhes, wriggles and twists in response to the presence of skin and force. The robot is animated only when actively engaged by a person, otherwise it is at rest. Stroking, rubbing or grasping ADB results in it pushing back, retreating or occasionally grasping onto a body part, depending on the combination of stimulus. Participants may experience the object at their leisure. They can play with the device, exploring how it feels, and how it responds to their touch.

JEFFREY SHAW
Disappearance
In this work the movement of a large video monitor mounted on an industrial fork-lift truck creates a virtual representation of a larger than life size ballerina. As the forklift moves the monitor up and down the ballerina is presented from head to toe, and as the forklift truck rotates the ballerina also appears to turn. In this way the monitor functions as a window that gradually reveals the virtual presence of the ballerina who is dancing in the same axis as the rotating forklift truck. Also visible inside the motor compartment of the forklift truck is a small rotating ballerina figurine in front of which a video camera moves up and down. This mechanism is electronically synchronised with the movement of the forklift itself and provides the closed circuit source for the video image of the ballerina that is seen on the monitor screen. Disappearance evokes and celebrates the memory of the ballerina on a music box (a first generation robot) and generates her virtual reconstruction to the extent that the machinery of reproduction itself now incarnates her pirouettes.
video
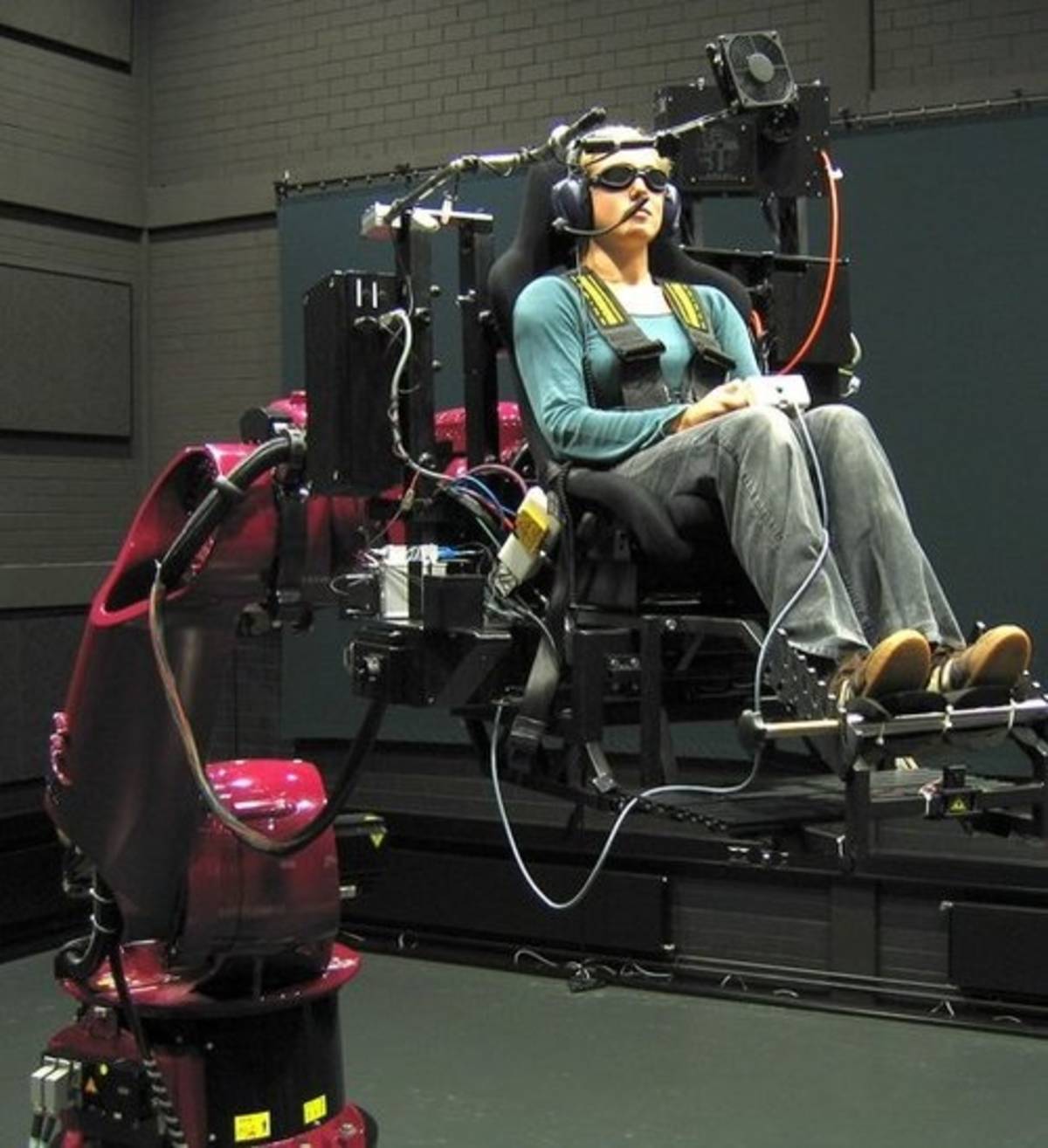

CyberMotion Simulator
Max-Planck-Institut
The CMS consists of an industrial robot arm with six independent axes, extended with an L-shaped cabin axis. The seventh axis allows for varying the orientation of the cabin with respect to the robot arm by changing the location of the cabin’s attachment point from behind the seat to under the seat, or any intermediate position. Recently, the CMS has been further extended with a linear axis of ten meters. The resulting eight degrees-of-freedom (DOF) provide an exceptionally large workspace. Several extreme motions and positions can be achieved, such as large lateral/longitudinal motions, sustained centrifugal motions, infinite head-centered rotation, and up-side-down motions.

Auke Ijspeert
Roombot
Biorobotics Laboryator
The individual Roombots are about the size of fat grapefruits, but one day they could be much smaller. Vespignani and his fellow researchers are investigating ways for the bots to communicate among themselves, like bacteria. In a hundred years, maybe the individual units will be so small as to be microscopic–and instead of summoning 10 friendly robots from different corners of the room, a person could summon something as nebulous and numerous as an army of technological spores.

Tod Machover
Death and the Powers
Science fiction and poignant family drama combine in one of the most stunning, cutting-edge operas of the 21st century, with a libretto by former Poet Laureate Robert Pinsky, coming to the stage of the Winspear Opera House in a production directed by Diane Paulus, designed by Alex McDowell (Steven Spielberg’s Minority Report) and conducted by Nicole Paiement (TDO’s The Lighthouse).This visually spectacular robot pageant by MIT Media Lab’s Tod Machover tells the story of a terminally ill billionaire, sung by Robert Orth, who downloads his consciousness into “the System” and proceeds to use all his powers to persuade his loved ones to join him there. Without bodies, without the possibility of touch, sex, suffering, and death — are we still genuinely human?Explore these existential questions and much more in a piece Variety described as “playful, lyrical and…mesmerizing.” Also starring Joélle Harvey as Miranda, Patricia Risley as Evvy, and Hal Cazalet in his Dallas Opera debut as Nicholas.
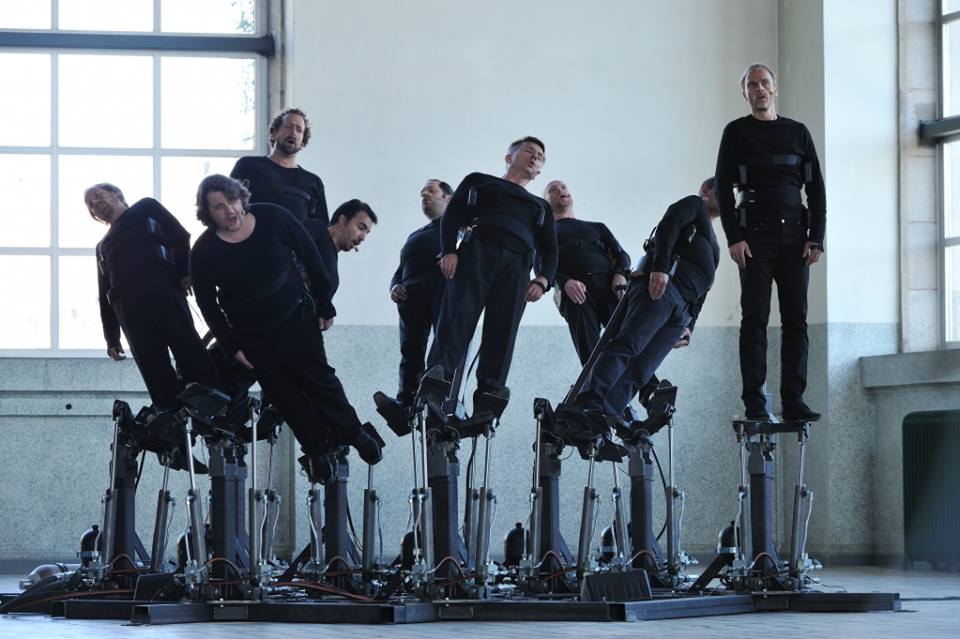

Cod.Act
振り子の合唱団
Pendulum Choir
Pendulum Choir is an original choral piece for 9 A Cappella voices and 18 hydraulic jacks. The choir stands on tilting platforms, constituting a living, sonorous body. That body expresses itself through various physical states. Its plasticity varies at the mercy of its sonority. It varies between abstract sounds, repetitive sounds, and lyrical or narrative sounds. The bodies of the singers and their voices play with and against gravity. They brush and avoid each other creating subtle vocal polyphonies. Or, supported by electronic sounds, they break their cohesion and burst into lyrical flight or fold up into an obsessional and dark ritual. The organ travels from life to death in a robotic allegory where the technological complexity and the lyricism of the moving bodies combine into a work with Promethean accents.

GUY BEN-ARY, PHILIP GAMBLEN AND STEVE POTTER
Silent Barrage
Silent Barrage has a “biological brain” that telematically connects with its “body” in a way that is familiar to humans: the brain processes sense data that it receives, and then brain and body formulate expressions through movement and mark making. But this familiarity is hidden within a sophisticated conceptual and scientific framework that is gradually decoded by the viewer. The brain consists of a neural network of embryonic rat neurons, growing in a Petri dish in a lab in Atlanta, Georgia, which exhibits the uncontrolled activity of nerve tissue that is typical of cultured nerve cells. This neural network is connected to neural interfacing electrodes that write to and read from the neurons. The thirty-six robotic pole-shaped objects of the body, meanwhile, live in whatever exhibition space is their temporary home. They have sensors that detect the presence of viewers who come in. It is from this environment that data is transmitted over the Internet, to be read by the electrodes and thus to stimulate, train or calm parts of the brain, depending on which area of the neuronal net has been addressed.

satoru sugihara
A(g)ntense gallery installation
ATLV is a computational design firm based in los angeles, california. Founded by satoru sugihara, the studio pushes the boundaries of practice and research in contemporary architecture and spatial design. Through integration of technological innovations, design problems can be approached with many different perspectives. Using tailored software tools, ATLV is able to employ algorithms alongside electronic hardware and robotics to seek broader ideas of design, fabrication, and process.
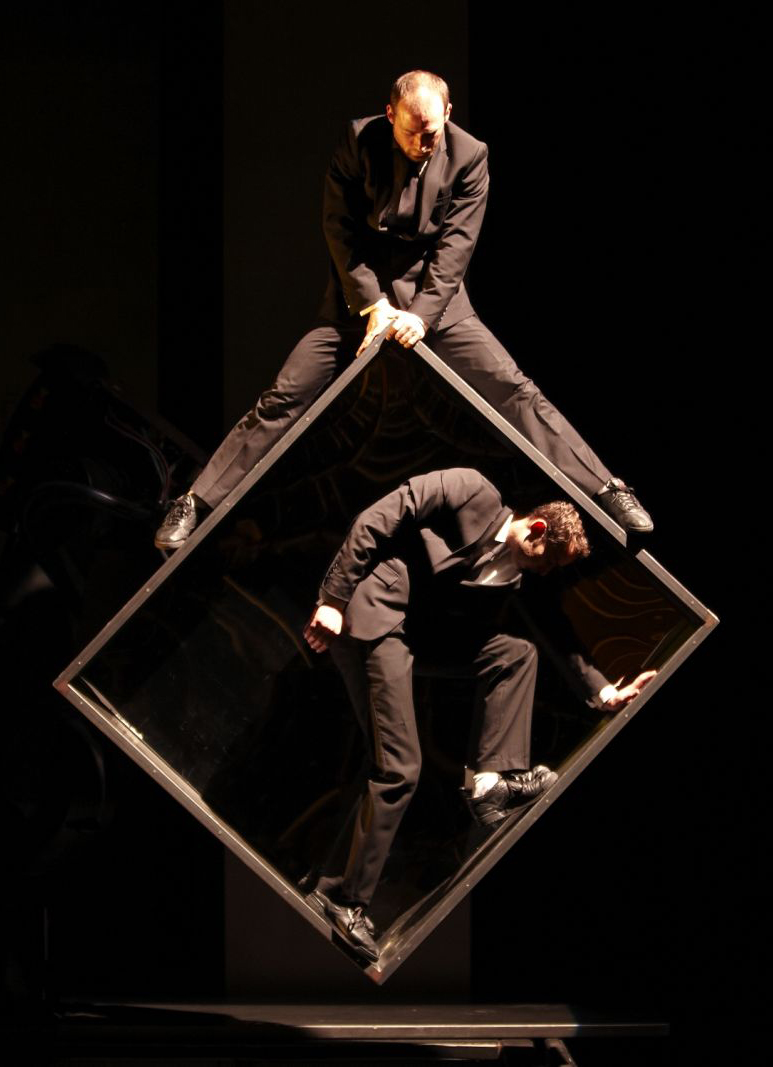

Aurélien Bory
Sans Objet
“Avec Sans objet j’ai voulu introduire sur scène un robot industriel ayant la force de déplacer des éléments de décor aussi bien que des acteurs. La machine devient un protagoniste à part entière. Il s’agit d’un bras articulé, mécanique. On l’utilise comme une « marionnette » – un être 100% technologique – dans son dialogue avec un homme contemporain ordinaire.”

xenobots
Xenobots – the First “Living Robots”
Researchers used the Deep Green supercomputer cluster and an evolutionary algorithm to design new life-forms that could achieve an assigned task. Then they built them by combining together different biological tissues from Xenopus laevis embryos, hence the name Xenobots.
Credit:A scalable pipeline for designing reconfigurable organisms
Sam Kriegman, Douglas Blackiston, Michael Levin, and Josh Bongard
PNAS, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1910837117

bart hess
바트 헤스
巴特·赫斯
בארט הס
БАРТА ХЕССА
SIlVERNanine Linning
Nothing has changed as radically in the last few decades as the technology we surround ourselves with on a daily basis. Modern means of communication let the world shrink to a pocket size Global Village. Medical technology promises life beyond its natural limits. Robotics, cybernetics and developments in the field of artificial intelligence put the equally fascinating as disquieting idea of artificial life within our grasp. Nanine Linning’s new production SILVER addresses the intimate – and increasingly intrusive – relationship between the human and the technological, showing the beauty of its aesthetics, but also questioning its promise of ever increasing progress and self-improvement.
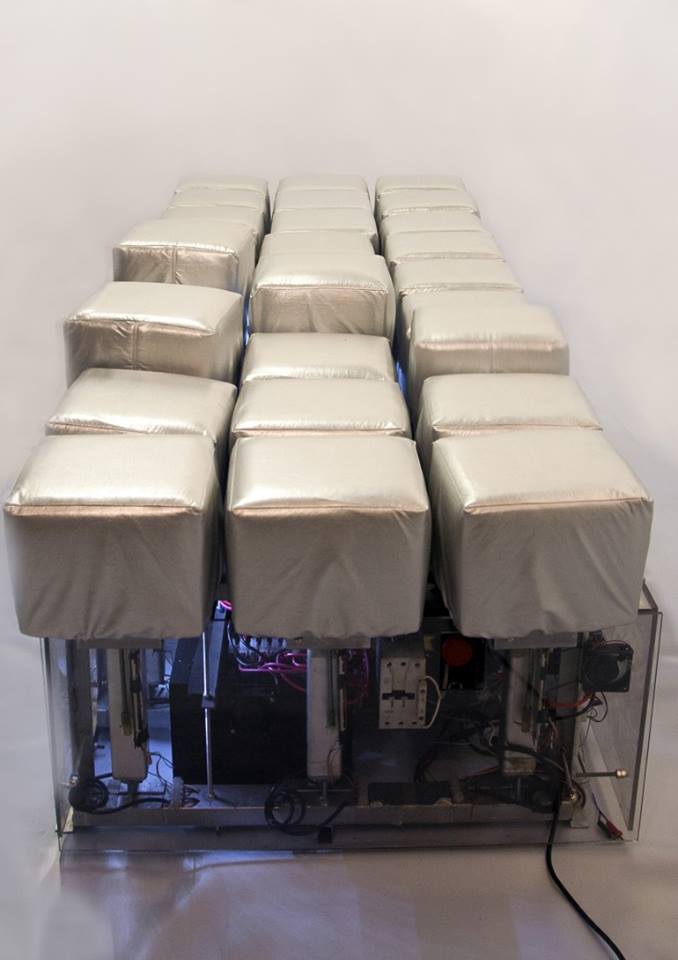

Ricardo Barreto and Maria Hsu Rocha
Martela
FILE FESTIVAL
Tactila is an art form whose medium is the sense of touch (tact) which is independent from the all the other ones and has its own intelligence, imagination, memory, perception, and sensation. It is well known that vision and sound have hegemony in arts and in other disciplines. Tactila takes place in time and, therefore, can be recorded and have various forms of notation for subsequent executions. That is why its development became possible only now, thanks to mechatronic and robotic systems which are compatible with machine languages.
The creation of tactile works involves a (tact) composition, which can be made through handmade notation and played on a keyboard or directly on the computer of the tactile machine ( robot ).
Tactile machines can present numerous tactile possibilities through points, vectors, and textures with varying rhythms and intensities, and be run in different extensions and locations of our body.
.
The first tactile machine is called “Martela”. It is a tactile robot comprised of 27 engines subdivided into three squares (3 x 3), i.e., each square has 9 engines. Each engine corresponds to a matrix point, so we have 27 tactile units that allow to touch the user’s body with various intensities.

BILL VORN
DSM-VI
DSM-VI est une suite logique à notre approche artistique de création de mondes artificiels et de systèmes entièrement robotiques. Cette fois, nous voulons créer un univers qui met en scène des créatures exprimant des symptômes de comportements psychologiques «anormaux» et confrontés à de graves problèmes de «santé mentale», tels que névrose, psychose, troubles de la personnalité, paranoïa, schizophrénie, dépression, délire, etc. formes de comportement et troubles mentaux. Le titre du projet est inspiré du célèbre manuel de référence publié par l’American Psychiatric Association, le DSM-IV. Le DSM-IV (Manuel diagnostique et statistique des troubles mentaux) est considéré comme la bible de la psychiatrie moderne. Tantôt glorifié tantôt fortement critiqué, il s’agit d’un ouvrage de représentation qui décrit et classe les troubles du comportement humain et les maladies mentales. La version IV du DSM a été publiée en 1994 puis révisée en 2000. La version V est actuellement en préparation et devrait à terme être publiée en 2012. Avec ce projet, nous proposons la version VI. A l’instar de certains de nos précédents travaux conçus autour de l’idée de «la misère des machines» (voir La cour des miracles), le projet DSM-VI veut poursuivre notre travail de création sur la métaphore du vivant en interrogeant désormais la notion d’une «psychose des machines».

elevenplay + rhizomatiks research
fly
Aqui, os drones são usados de forma mais cuidadosa: eles são holofotes robóticos. Reconfigurando continuamente sua posição em torno de um único dançarino humano, o conjunto produz um jogo hipnotizante de sombra e luz.É mais do que um truque legal. Em vez de ter drones no palco apenas por tê-los, o clipe mostra como as máquinas podem ser usadas de maneiras mais sutis e expressivas. Ser capaz de coreografar as três fontes de luz que se movem independentemente em torno de um artista, presumivelmente, permite que você crie todos os tipos de efeitos visuais que você simplesmente não conseguiria de outra forma. No início, os drones piscam suas luzes em sequência, projetando um filme de stop motion nas sombras na parede atrás. Depois disso, eles exploram outras configurações ao redor da dançarina: iluminando-a, escondendo-a e revelando-a novamente em silhueta.

PAOLA GAETANO-ADI
Desiring Machine: and/or the female reincarnation of Sisyphus
Née en Argentine, Paula Gaetano Adi est artiste et chercheure dans les domaines de la sculpture, de la performance, et des installations interactives et robotiques. Elle utilise le corps humain et non humain comme point de départ de ses recherches, et s’intéresse aux effets discursifs et aux impacts affectifs des technosciences sur la subjectivité humaine et dans l’art. Ses œuvres ont été présentées sur la scène internationale à Beijing, Berlin, Madrid, Moscou, Stockholm, São Paulo, New York, Poznan et Buenos Aires, entre autres. Elle a reçu de nombreux prix et bourses, tels que le premier prix à la compétition VIDA 9.0 sur l’art et la vie artificielle, organisée par la Fundación Telefónica, et le premier prix LIMbØ du Musée d’art moderne de Buenos Aires, la bourse Fergus Memorial en 2009 et 2010 de même que la bourse accordée à un artiste ibéro-américain dans le cadre de la compétition VIDA 14.0. À l’heure actuelle, Paula Gaetano Adi est professeure adjointe dans le programme de Studio Art du College of Visual Arts and Design de l’Université de North Texas, où elle coordonne le secteur réservé aux nouveaux médias. À cette université, elle s’est également jointe au groupe Initiative for Advanced Research in Technology and the Arts (iARTA).

Ricardo Barreto and Maria Hsu
Avactor (A.I.)
FILE FESTIVAL
Thus, we could define computers not only as object-machines for the use of natural subjectivity, but also as machines of artificial subjectivity, in such way that the subject- machines would operate the object-machines, the same happening for automata, robots and digital avatars. However, we observe the need of another element, whose absence prevents artificial subjectivity’s manifestation. In the present moment, rather than an artificial ego or an artificial conscience, in a structuralizing sense, it must have, in a tactical sense, a persona or a personality, in sum, an actor. Without that persona, artificial subjectivity becomes a mere landscape, lacking subjective referential; without that actor, there is not empathy between artificial subjectivity and natural subjectivity. We call that artificial personality: the Avactor.

ALAN RATH
آلان راث
Watcher VIII
Alan Rath erkundet die Schnittstelle von Kunst und Technologie und macht Elektronik mit seinen elektrischen, kinetischen und Roboterskulpturen zu einer Kunstform. Wall Throbber (1998) zum Beispiel ist ein Gerät aus Aluminium, Elektronik, einem Lautsprecher und Leuchten, bei dem eine rote Kugel sanft abprallt. Neuere Arbeiten enthalten digitale Medien wie bewegte Bilder auf eine Weise, die die Technologie humanisiert. In Watcher VII (2011) zeigen zwei Bildschirme Nahaufnahmen ausdrucksstarker menschlicher Augen, die aus beiden Seiten einer anthropomorphen Weißmetallstruktur herausragen. Er verleiht diesen Skulpturen lebensechte Qualitäten und geht davon aus, dass Menschen menschliche Qualitäten auf Aufforderung auf Maschinen projizieren und sie sogar als Persönlichkeiten wahrnehmen. Die Arbeit zelebriert das Potenzial der Technologie für das Gute und spielt gleichzeitig auf die Gefahren an, die unter der Oberfläche lauern.

Raffaello D’Andrea and Max Dean
The Table
The Table is an autonomous robot with an automatic mechanized system able to react to unexpected movement or obstacles and to carry out one or more tasks by executing a program in a given environment. As is the case with most “prototypical” robotic works, or single editions, the basic physical components can be pre-manufactured then modified or custom built to meet specific needs. In the case of The Table, the control system and its algorithms were entirely conceived by Max Dean and Raffallo D’Andrea. All the components, including the wheels and motors, were also custom manufactured, giving the installation a unique character. The singular characteristic of this work lies in the robotic nature of the table and it’s capacity to operate in an environment specifically designed for it. For example, the shade of red painted on the floor is directly linked to the effective functioning of the camera and the control software. Also, the space lights used in the room produce a light that prevents the creation of shadows, which the software could mistakenly interpret as a physical presence.

Michael Najjar
史上第一位進入太空的藝術家
laokoon, from the work series “bionic angel”
„Bionischer Engel“ Die Arbeitsreihe „Bionischer Engel“ geht von der zukünftigen Transformation und technologischen Kontrolle der menschlichen Evolution aus. Die rasante Entwicklung auf dem Gebiet der sogenannten „g-r-i-n-Technologien“ (Genetik, Robotik, Information und Nanotechnologie) verändert unseren Körper, Geist, Erinnerungen und Identitäten, wirkt sich aber auch auf unsere Nachkommen aus. Diese Technologien laufen alle zusammen, um die menschliche Leistung zu verbessern. Durch die pränatale genetische Bestimmung können Kinder nach Plan gebaut werden. Klonkörper werden zu Aufbewahrungsorten für Ersatzorgane, während durch Manipulation der Atomstruktur neue Körper entstehen, die die alten in Bezug auf Robustheit, Elastizität und Haltbarkeit weit übertreffen. Die neuen Karosserien sind an die Bedürfnisse der Hochgeschwindigkeitsdatenautobahn angepasst. Diese Entwicklungen, die auf genetischen Algorithmen und neuronalen Netzwerken basieren, ermöglichen es nun, die biologische Evolution zu steuern. Sie eröffnen dem Menschen den Weg zu einer neuen und überlegenen Existenzform.