Maxim Zhestkov
Simulation Hypothesis
In Simulation Hypothesis, Zhestkov equally seeks inspiration in pre-historic cultures of cave art and ancient bas-reliefs. He plays with a visuality that precedes written language, from a time in which early humans used clay to make vessels and figurines.
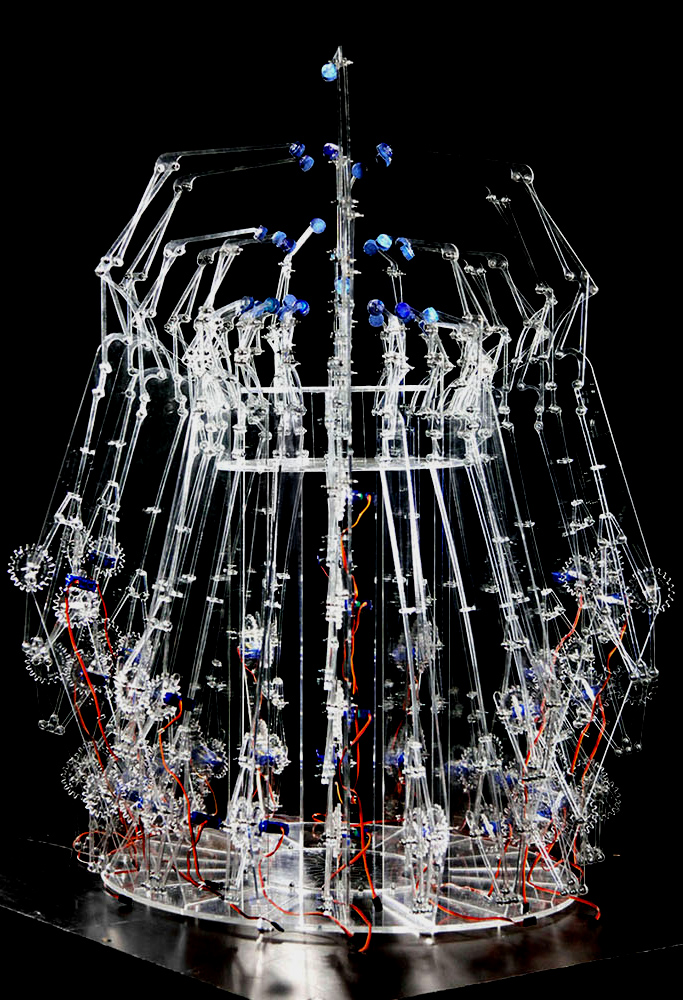
The artist uses the inspiration from ancient forms of art and transforms it into digital sculptures using simulations and algorithms based on principles of nature.
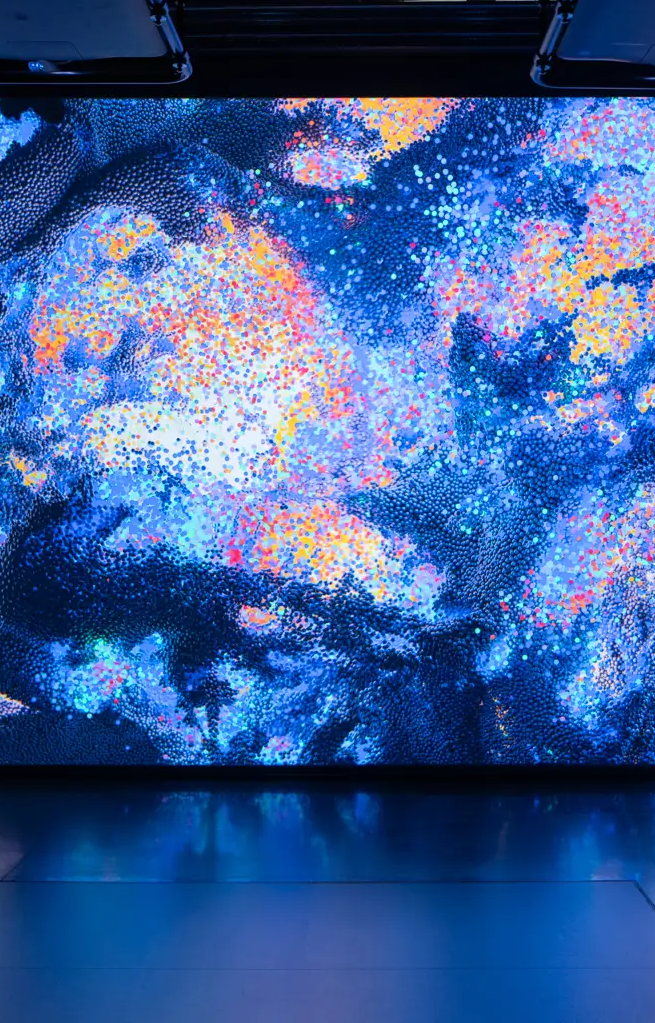
The show takes viewers on a conceptual journey, immersing them first in Clouds of Creation, a large-scale projection that recreates the Big Bang, and then guiding them through micro manifestations of this transformative moment of genesis.